Marijuana Side Effects
Marijuana is an increasingly accepted drug which has been legalized in 9 states for recreational use. With as many as 61% of Americans supporting further legalization, acceptance of the drug is at an all-time high. That's not a surprise, considering 52% of Americans admit to having tried cannabis and most studies point to about 9.5% of the population being current users. However, with an estimated 2.9% of Americans qualifying under cannabis use disorder, marijuana's negative side effects are often much greater than users realize and can lead to changes in personality, work productivity, and can lead to a use disorder or addiction.
While cannabis has been proven to have positive side effects including medical benefits for diseases and anxiety, uncontrolled use or abuse of any drug can have negative impacts. For example, prescription pain pill abuse is rampant and often has many negative side effects. Marijuana use disorder is just one of the many ways cannabis abuse can affect you.
How Does Cannabis Affect You?
Marijuana or the dried flowers of cannabis (sativa or indica) contains more than 500 chemicals known as cannabidiols, the most common of which are THC and CBD. These cannabidiols bind with receptors in the brain to produce effects such as relaxation, a sense of well-being, anxiety, hallucinations, or a distorted sense of time. This happens when the cannabidiol stimulates the brain into producing dopamine at altered levels, creating a shift in how the user feels and thinks.
THC is the primary active compound here, making up about 60% of all active cannabidiols in cannabis. In addition, most strains of cannabis contain anywhere from 3% to 30% + THC, which means that the effects and mind-altering results of smoking or using marijuana can vary quite a bit from strain to strain.
Symptoms of Marijuana Use
Most marijuana users will display the same pattern of traits. However, exact behavior and symptoms of marijuana use will depend on duration and volume of use, the strain used, and how the cannabis is used. For example, smoking and eating marijuana products will have vastly different effects, with eating sometimes producing audio/visual hallucinations and lasting for several hours beyond that of smoking.
In most cases, marijuana side effects include:
- Lethargy or lassitude
- Inability to focus or concentrate (not prevalent with all strains)
- Increased creativity
- Red or glassy eyes
- Hunger (the munchies)
- Delayed reaction times
- Poor muscle coordination
- Panic and anxiety
- Increased heart rate
- Paranoia
- Dry mouth
- Poor memory
Users typically experience a sense of well-being and pleasure while high, typically want to do very little, and often eat somewhat uncontrollably.
Long-term Effects of Marijuana Use
Over the long-term, consistent marijuana use begins to change the patterns and structure inside the brain. This is normal of any consistent drug use and it will often cause negative side effects such as panic and anxiety to worsen over time.
- Paranoia
- Anxiety and panic
- Poor short-term memory
- High or lower blood pressure
- Acute psychosis
Long-term cannabis use can result in problems at work and school because of difficulty concentrating, poor coordination, or an inability to focus or remember. It can also contribute to lowered grades and results through reduced motivation and memory. However, not all strains will contribute to this sort of change in behavior and work output, as different levels of THC affect the brain in different ways.
Marijuana Toxicity
In some cases, marijuana may be cut with other drugs such as hallucinogenic, which can greatly increase the danger of the drug. Here, users may experience sudden spikes in heart rate or blood pressure, changes in breathing and respiration, chest pain and arrhythmia, seizures, stroke, or sudden collapse. In this case, the side effects are likely the result of another drug. It is crucial to get the user to medical care as quickly as possible.
Marijuana Use Disorder
While marijuana is not extremely toxic or harmful in the way that many other drugs are, it can cause use disorder and addiction. With an estimated 2.9% of the U.S. population suffering from cannabis use disorder, marijuana addiction is significantly more common than most assume. Cannabis use disorder is defined as the continued use of marijuana despite mild to significant impairment, where the user realizes cannabis is causing problems and continues to use anyway. Use disorder typically develops in the following stages:
Tolerance – The user develops a tolerance to cannabis and must smoke more and more to achieve the same affects or any affects at all. Increased usage contributes to further changes in dopamine and serotonin production in the brain, resulting in worsening side effects and symptoms.
Dependence – The body adjusts to changed levels of dopamine production in the body, resulting in a dampening effect on dopamine. When the user is not high, they may feel lethargic, numb, or even agitated and irritated. Ceasing marijuana use will result in withdrawal symptoms and cravings. This affects about 9% of long-term users who begin smoking as adults and about 21% who begin smoking as teens or minors.
Addiction – Users develop problematic behaviors from dependence and may suffer psychological, physical, or career and housing effects from cannabis use. The user is addicted and continues to abuse marijuana anyway.
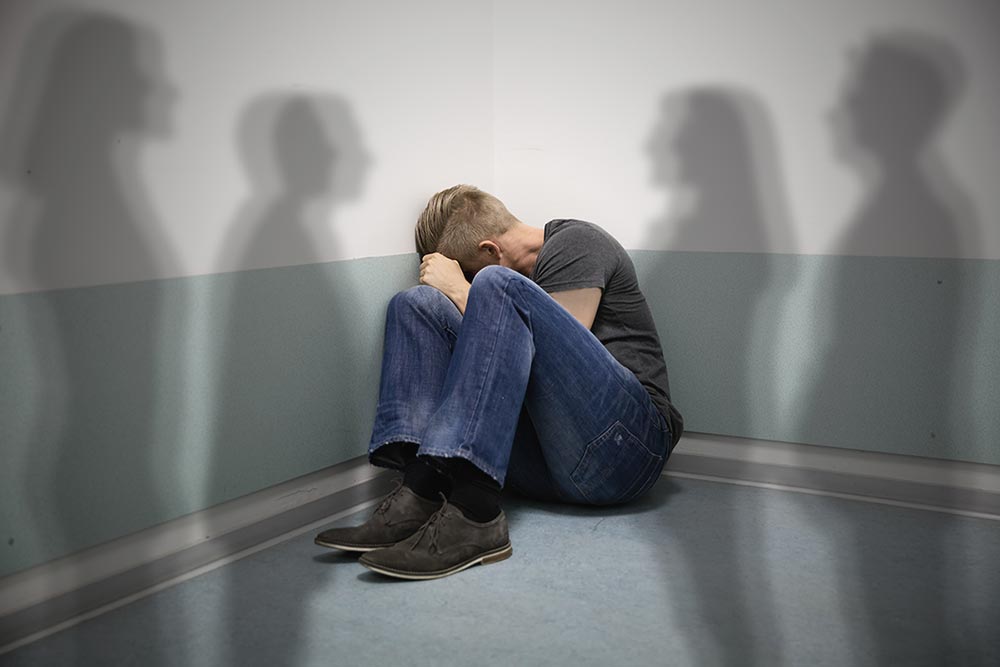
Marijuana Withdrawal
Marijuana withdrawal symptoms are typically similar to flu symptoms with sweating, chills, and a decreased appetite being the most common. While not everyone experiences marijuana withdrawal symptoms, long-term heavy users will almost always go through a withdrawal period marked by increased anxiety and agitation, nervousness, irritability or aggression, insomnia, bad dreams, weight loss, depression, headache, and often stomach pain. These symptoms can range from moderate to severe depending on the level of substance use and the user's metabolism and tolerance. Strong cravings are typically present as well and many users will experience a rebound effect.
You are at a heightened risk of marijuana withdrawal if you have smoked or used cannabis consistently for 3 or more months or experience cravings throughout the day when not using.
Getting Help for Marijuana Addiction
While marijuana use is increasingly accepted, dependence and addiction are a common problem. While not as dangerous as harder drugs such as heroin or even prescription pain pills, marijuana can cause deleterious mental effects including increased paranoia and anxiety, psychosis, and panic disorders. It also contributes to impaired thinking, inability to enjoy life, contributes to crime and criminal behavior, and to financial difficulties.
Getting clean means going through a drug detox process where you experience withdrawal in a controlled medical setting. Here, users are allowed to withdraw safely and comfortably with mental and emotional support to ensure that they move into recovery as quickly and safely as possible. Marijuana detox is followed up with behavioral therapy and counseling as well as group therapy to change the behaviors behind substance abuse. Trained therapists also work to help individuals recognize the social, emotional, and mental problems underlying addiction, so that they can take steps to fix them, learn coping mechanisms, and move on to a healthy life without drug use. Many cannabis addiction treatment programs also include support for dual diagnosis or cooccurring disorders to help individuals who are self-medicating to move forward with their lives.
Cannabis addiction can dramatically affect your life and that of everyone around you. If you or a loved one is addicted to cannabis, there is help. Feel free to contact us today about addiction treatment programs at our affordable drug and alcohol rehab that fit your needs. The Anaheim Lighthouse is a modern and effective addiction treatment center in Southern California.